Robotics technology has transformed various industries, and healthcare is no exception. In this article, we explore the significant role of robotics in healthcare, from surgical procedures to patient care and rehabilitation.
1. Introduction to Robotics in Healthcare
Robotics in healthcare involves the use of robotic systems to perform tasks traditionally carried out by humans in clinical settings. These systems are designed to assist healthcare professionals, improve patient outcomes, and enhance overall efficiency and safety in healthcare delivery.
2. Types of Robotics Used in Healthcare
Surgical robots
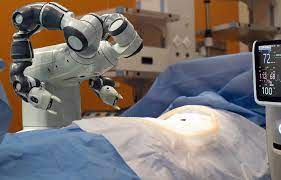
Surgical robots, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, assist surgeons in performing minimally invasive procedures with precision and control, leading to faster recovery times and reduced risk of complications.
Rehabilitation robots
Rehabilitation robots aid patients in recovering from injuries or surgeries by providing assistance and guidance during physical therapy sessions, promoting mobility, strength, and coordination.
Telepresence robots
Telepresence robots enable remote communication and interaction between healthcare providers and patients, allowing for virtual consultations, monitoring, and care delivery, particularly in remote or underserved areas.
Assistive robots
Assistive robots support elderly or disabled individuals in performing daily activities, such as bathing, dressing, and medication management, enhancing their independence and quality of life.
3. Applications of Robotics in Healthcare
Minimally invasive surgeries
Robotic-assisted surgery enables surgeons to perform complex procedures through small incisions with greater precision and dexterity, resulting in shorter hospital stays, less pain, and faster recovery for patients.
Physical therapy and rehabilitation
Rehabilitation robots assist patients in regaining motor function, strength, and range of motion after injuries, strokes, or surgeries, facilitating personalized and intensive therapy sessions tailored to individual needs.
Remote patient monitoring and telemedicine
Telepresence robots and remote monitoring devices enable healthcare providers to monitor patients’ vital signs, administer medication, and provide medical advice and support from a distance, improving access to healthcare services and reducing the need for in-person visits.
Elderly care and assistance
Assistive robots help elderly individuals with activities of daily living, such as mobility assistance, medication reminders, and companionship, enabling them to age in place and maintain independence while receiving necessary support.
4. Benefits of Robotics in Healthcare
Improved surgical precision and outcomes
Robotic-assisted surgery offers greater precision, stability, and control during procedures, leading to reduced trauma, blood loss, and post-operative complications, and improved clinical outcomes for patients.
Enhanced patient safety and comfort
Robotic systems minimize the risk of human error and variability in healthcare delivery, ensuring consistent and reliable performance, and enhancing patient safety, comfort, and satisfaction throughout the care continuum.
Increased accessibility to specialized care
Telepresence robots and remote monitoring technologies expand access to specialized healthcare services, enabling patients in rural or underserved areas to receive timely diagnosis, treatment, and support from expert providers regardless of geographic location.
Augmented healthcare workforce efficiency
Robotics technology augments the capabilities of healthcare professionals, enabling them to focus on higher-value tasks, such as clinical decision-making and patient interaction, while delegating routine or repetitive tasks to robotic systems, thereby improving workflow efficiency and productivity.
5. Challenges and Limitations
High cost of robotic systems
The initial investment and maintenance costs associated with robotic technology can be prohibitive for healthcare institutions, limiting widespread adoption and accessibility, particularly in resource-constrained settings.
Regulatory and ethical concerns
Regulatory approval, patient safety, and ethical considerations, such as privacy, autonomy, and liability, pose challenges to the integration and deployment of robotics in healthcare, requiring careful oversight and compliance with established guidelines and standards.
Integration with existing healthcare infrastructure
Integrating robotics technology with existing healthcare systems, workflows, and electronic health records presents technical challenges, interoperability issues, and resistance to change, requiring collaboration and coordination among stakeholders.
Training and adoption barriers
Training healthcare professionals to use and trust robotic systems effectively, overcoming skepticism, and resistance to new technologies, and ensuring user proficiency and competence pose significant barriers to the adoption and implementation of robotics in healthcare.
6. Future Outlook and Innovations
Despite the challenges, the future of robotics in healthcare is promising, with ongoing advancements in technology, artificial intelligence, and human-robot interaction, driving innovation, affordability, and accessibility. Future developments may include smarter, more adaptive robotic systems capable of autonomous decision-making and personalized care delivery.
Conclusion
In conclusion, robotics technology is revolutionizing healthcare delivery, offering unprecedented opportunities to improve patient outcomes, enhance efficiency, and expand access to quality care. By leveraging robotics in surgical procedures, rehabilitation, telemedicine, and elderly care, healthcare organizations can address current challenges, drive innovation, and shape the future of healthcare delivery.